CCNA Discovery 2 Module 4 Exam Answers V4.0
0 comments Posted by GOSSIP - HOT 247 [d0t] Us at 12:59 PM
• 128
• 254
• 255
• 256
• 512
• 1024
2. Convert the decimal number 231 into its binary equivalent. Select the correct answer from the list below.
• 11110010
• 11011011
• 11110110
• 11100111
• 11100101
• 11101110
3. How many usable hosts are available given a Class C IP address with the default subnet mask?
• 254
• 255
• 256
• 510
• 511
• 512
4. Which statement describes NAT overload or PAT?
• Each internal address is dynamically translated to an individual external IP address.
• A single internal address is always translated to the same unique external IP address.
• Many internal addresses can be translated to a single IP address using different port assignments.
• Many internal addresses are statically assigned a single IP address and port to use for communications.
5. Which IPv4 class of addresses provides the most networks?
• Class A
• Class B
• Class C
• Class D
• Class E
6. Which statement accurately describes public IP addresses?
• Public addresses cannot be used within a private network.
• Public IP addresses must be unique across the entire Internet.
• Public addresses can be duplicated only within a local network.
• Public IP addresses are only required to be unique within the local network.
• Network administrators are free to select any public addresses to use for network devices that access the Internet.
7. Which two statements describe classful IP addresses? (Choose two.)
• It is possible to determine which class an address belongs to by reading the first bit.
• The number of bits used to identify the hosts is fixed by the class of the network.
• Only Class A addresses can be represented by high-order bits 100.
• Up to 24 bits can make up the host portion of a Class C address.
• Up to 24 bits can be used to identify unique networks.
• Three of the five classes of addresses are reserved for multicasts and experimental use.
8. Company XYZ uses a network address of 192.168.4.0. It uses the mask of 255.255.255.224 to create subnets. What is the maximum number of usable hosts in each subnet?
• 6
• 14
• 30
• 62
9. hat is the network broadcast address for a Class C address of 192.168.32.0 with the default subnet mask?
• 192.168.0.0
• 192.168.0.255
• 192.168.32.0
• 192.168.32.254
• 192.168.32.255
10.
Refer to the exhibit. Host A is connected to the LAN, but it cannot get access to any resources on the Internet. The configuration of the host is shown in the exhibit. What could be the cause of the problem?
• The host subnet mask is incorrect.
• The default gateway is a network address.
• The default gateway is a broadcast address.
• The default gateway is on a different subnet from the host.
11. IPv6 increases the IP address size from 32 bits to how many bits?
• 64
• 96
• 128
• 192
• 256
• 512
12. What is the range of the first octet in a Class B address?
• 127 to 191
• 127 to 192
• 128 to 191
• 128 to 192
13. Which IPv4 class provides the highest number of host addresses per network?
• Class A
• Class B
• Class C
• Class D
• Class E
14.
refer to the exhibit. Which range of IP addresses would allow hosts that are connected to the Router1 Fa0/0 interface to access outside networks?
• 192.168.1.0 through 192.168.1.95
• 192.168.1.66 through 192.168.1.94
• 192.168.1.66 through 192.168.1.96
• 192.168.1.0 through 192.168.1.127
• 192.168.1.66 through 192.168.1.128
15. Which option shows the proper notation for an IPv6 address?
• 2001,0db8,3c55,0015,abcd,ff13
• 2001-0db8-3c55-0015-abcd-ff13
• 2001.0db8.3c55.0015.abcd.ff13
• 2001:0db8:3c55:0015::abcd:ff13
16. What are two reasons that NAT was developed? (Choose two.)
• to preserve registered public IP addresses
• to allow users on the public Internet to access local networks
• to provide a method for privately addressed LANs to participate in the Internet
• to make routing protocols operate more efficiently
• to allow private addresses to be routed on the public Internet
• to reduce overhead and CPU usage on gateway routers
17. What must happen for a privately addressed host on an inside local network to be able to communicate with an outside destination host on the Internet?
• The host IP address must be translated to an outside private address.
• The host IP address must be translated to an inside local address.
• The host IP address must be translated to an outside local address.
• The host IP address must be translated to an inside global address.
18. Which port numbers are used by PAT to create unique global addresses?
• 255 and below
• 1024 and below
• 1025 and above
• 64,000 and above
19. Static NAT works by mapping a specific inside local IP address to what other specific address type?
• inside global
• outside local
• outside global
• private IP address
20. What are three advantages of NAT implementations? (Choose three.)
• improved security
• improved router performance
• decreased processor load
• improved scalability
• universal application compatibility
• sharing few public IP addresses with many hosts
Labels: CCNA Discovery 2
CCNA Discovery 2 Module 3 Exam Answers V4.0
0 comments Posted by GOSSIP - HOT 247 [d0t] Us at 12:59 PM
CCNA Discovery 2 Module 3 Exam Answers Version 4.0
• faster communication speeds
• improved physical security
• more resistant to hacker attempts
• centralized cable management
• less electrical usage
2. Which three issues should be noted on the technician's site survey report? (Choose three.)
• unlabeled cables
• only two power outlets per wall in each room
• poor physical security of network devices
• horizontal cabling runs under 100 meters
• lack of UPS for critical devices
• two users sharing the same computer
3. Which two types of cable are used for initial router configuration? (Choose two.)
• serial cable
• rollover cable
• straight-through cable
• crossover cable
• patch cable
• console cable
4. In addition to the inventory sheet, what other information about the hosts and networking equipment should be documented by the on-site technician while performing the site survey?
• any obsolete office equipment being stored
• all product keys for site license software
• any planned growth anticipated in the near future
• the memory requirements for installed application software
5.
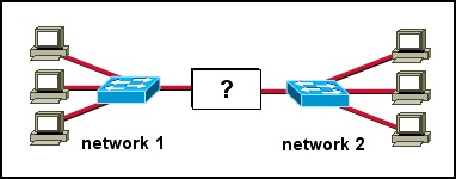
Refer to the exhibit. What type of device is used to connect two networks?
• hub
• router
• switch
• access point
6. It is said that the goal for availability of a communications system is "five-9s". What is meant by this?
• A down time of .00001% is unacceptable.
• A network needs to be available 99.999% of the time.
• Five percent of all network expense covers 99% of user requirements.
• The most critical time for network availability is from 9:00 to 5:00 p.m. five days a week.
• The best time to do maintenance on a network is from 5:00 p.m. to 9:00 a.m. five days a week.
7. What three things are included in a logical topology document? (Choose three.)
• the location of cables, computers, and other peripherals
• the path that the data takes through a network
• the wireless signal coverage area
• the wiring closet and access point locations
• the device names and Layer 3 addressing information
• the location of routing, network address translation, and firewall filtering
8. Which device has the ability to break up broadcast and collision domains?
• repeater
• hub
• router
• switch
9. Why is it important to review the results of an on-site survey report with the customer before beginning the network design?
• to inform the customer of how much time the upgrade will take
• to discuss the implementation schedule for the new equipment
• to verify that the report accurately describes the current network and any plans for expansion
• to layout the new network design and discuss possible equipment upgrades and replacements
10. A client requires a networking device that is capable of expansion to suit growing network demands. What type of device will suit this requirement?
• a networking device with ports that can be activated and deactivated
• a networking device with a modular physical configuration
• a networking device with the ability to be turned off remotely
• a networking device with a cost per port that is as high as possible
11. What does the use of redundant network components supply to a network?
• scalability
• manageability
• compatibility
• reliability
12. What is the benefit for a company to use an ISR router?
• An ISR provides the functionality of a switch, router, and firewall in one device.
• ISRs use a PC operating system for routing traffic, thus simplifying configuration and management.
• An ISR is immune to security attacks by hackers and so replaces all other network security measures.
• ISRs make routing decisions at OSI Layer 7, thus providing more intelligence to the network than do other routers.
13. Which three items are typically found in an MDF? (Choose three.)
• user workstations
• switches and routers
• fax machines
• network equipment racks
• the point of presence
• copier
14. What are two advantages of having ISP-managed services? (Choose two.)
• does not require leasing costs for service
• can guarantee up to 99.999% availability
• eliminates the need for data backup
• increases availability of help desk services
• does not require a Service Level Agreement
15. A manufacturing company is in the process of a network upgrade. Which two statements are true about the phases of the upgrade process? (Choose two.)
• Phase 1 is used to determine network requirements.
• Phase 2 includes creating an analysis report.
• Phase 3 is based on an implementation schedule that allows extra time for unexpected events.
• Phase 4 is where prototypes are created and tested.
• Phase 5 includes identifying and addressing any weaknesses in the design.
16. When designing a network upgrade, which two tasks should the onsite technician perform? (Choose two.)
• configure the servers and routers prior to delivery
• upgrade the network operating system and all client operating systems
• investigate and document the physical layout of the premises
• document the final design for approval by the customer
• perform a site survey to document the existing network structure
17. What is the term for the location at the customer premise where the customer network physically connects to the Internet through a telecommunications service provider?
• backbone area
• point of presence
• network distribution facility
• intermediate distribution frame
18.

to the exhibit. Which type of twisted pair cable is used between each device?
• A=console, B=straight, C=crossover, D= crossover, E=straight
• A=straight, B=straight, C=straight, D=crossover, E=console
• A=crossover, B=straight, C=straight, D=crossover, E=crossover
• A=console, B=straight, C=straight, D=crossover, E=crossover
• A=console, B=crossover, C=crossover, D=straight, E=straight
19. In what two ways will entering into a managed service agreement with an ISP for a network upgrade affect the costs that are incurred by the customer? (Choose two.)
• Customer IT training costs will increase to enable operation of the new equipment.
• The cost of hardware repairs and support will become the responsibility of the customer.
• Network upgrade and maintenance costs will become predictable.
• Staffing costs will increase because the customer will need to hire additional IT staff to complete the upgrade.
• The company will not need to spend a large amount of money to purchase the equipment upfront.
20. Which type of cable has a solid copper core with several protective layers including PVC, braided wire shielding, and a plastic covering?
• STP
• UTP
• coaxial
• fiber optic
21. What must be added when a network expands beyond the coverage area of the current telecommunications room?
• MDF
• POP
• IDF
• IXP
Labels: CCNA Discovery 2
CCNA Discovery 2 Module 2 Exam Answers V4.0
0 comments Posted by GOSSIP - HOT 247 [d0t] Us at 12:58 PM
• placing electrical signals on the medium for transmission
• initiating the network communication process
• encrypting and compressing data for transmission
• segmenting and identifying data for reassembly at the destination
• choosing the appropriate path for the data to take through the network
2. Which is a function of the transport layer of the OSI model?
• routes data between networks
• converts data to bits for transmission
• delivers data reliably across the network using TCP
• formats and encodes data for transmission
• transmits data to the next directly connected device
3. Which common Layer 1 problem can cause a user to lose connectivity?
• incorrect subnet mask
• incorrect default gateway
• loose network cable
• NIC improperly installed
4. Which three command line utilities are most commonly used to troubleshoot issues at Layer 3? (Choose three.)
• ping
• a packet sniffer
• Telnet
• ipconfig
• Traceroute
5. Which address is used by the router to direct a packet between networks?
• source MAC address
• destination MAC address
• source IP address
• destination IP address
6. What is the correct encapsulation order when data is passed from Layer 1 up to Layer 4 of the OSI model?
• bits, frames, packets, segments
• frames, bits, packets, segments
• packets, frames, segments, bits
• segments, packets, frames, bits
7. What are two goals of the ISP help desk? (Choose two.)
• conserving support resources
• network optimization
• competitive scalability
• customer retention
• sales of network services
8. In what two ways do Level 1 and Level 2 help desk technicians attempt to solve a customer's problems? (Choose three.)
• talking to the customer on the telephone
• upgrading hardware and software
• using various web tools
• making an onsite visit
• installing new equipment
• with remote desktop sharing applications
9. A customer calls the help desk about setting up a new PC and cable modem and being unable to access the Internet. What three questions would the technician ask if the bottom-up troubleshooting approach is used? (Choose three.)
• Is the NIC link light blinking?
• What is the IP address and subnet mask?
• Can the default gateway be successfully pinged?
• Is the network cable properly attached to the modem?
• Is the Category 5 cable properly connected to the network slot on the PC?
• Can you access your e-mail account?
10. A customer calls to report a problem accessing an e-commerce web site. The help desk technician begins troubleshooting using a top-down approach. Which question would the technician ask the customer first?
• Can you access other web sites?
• Is there a firewall installed on your computer?
• What is your IP address?
• Is the link light lit on your NIC card?
11. Which statement describes the process of escalating a help desk trouble ticket?
• The help desk technican resolves the customer problem over the phone and closes the trouble ticket.
• Remote desktop utilities enable the help desk technician to fix a configuration error and close the trouble ticket.
• After trying unsuccessfully to fix a problem, the help desk technician sends the trouble ticket to the onsite support staff.
• When the problem is solved, all information is recorded on the trouble ticket for future reference.
12. What are two functions of the physical layer of the OSI model? (Choose two.)
• adding the hardware address
• converting data to bits
• encapsulating data into frames
• signal generation
• routing packets
13. A customer calls the ISP help desk after setting up a new PC with a cable modem but being unable to access the Internet. After the help desk technician has verified Layer 1 and Layer 2, what are three questions the help desk technician should ask the customer? (Choose three.)
• What is your subnet mask?
• What is your IP address?
• Is the NIC link light blinking?
• Can you ping the default gateway?
• Is the network cable properly attached to the cable modem?
• Is the network cable correctly connected to the network port on the PC?
14. Which scenario represents a problem at Layer 4 of the OSI model?
• An incorrect IP address on the default gateway.
• A bad subnet mask in the host IP configuration.
• A firewall filtering traffic addressed to TCP port 25 on an email server.
• An incorrect DNS server address being given out by DHCP.
15. What are two basic procedures of incident management? (Choose two.)
• opening a trouble ticket
• using diagnostic tools to identify the problem
• surveying network conditions for further analysis
• configuring new equipment and software upgrades
• adhering to a problem-solving strategy
• e-mailing a problem resolution to the customer
16. Which level of support is supplied by an ISP when providing managed services?
• Level 1
• Level 2
• Level 3
• Level 4
17. What is the first step that is used by a help desk technician in a systematic approach to helping a customer solve a problem?
• identify and prioritize alternative solutions
• isolate the cause of the problem
• define the problem
• select an evaluation process
18. A network technician has isolated a problem at the transport layer of the OSI model. Which question would provide further information about the problem?
• Do you have a firewall that is configured on your PC?
• Do you have a link light on your network card?
• Is your PC configured to obtain addressing information using DHCP?
• What default gateway address is configured in your TCP/IP settings?
• Can you ping http://www.cisco.com?
19. An ISP help desk technician receives a call from a customer who reports that no one at their business can reach any websites, or get their e-mail. After testing the communication line and finding everything fine, the technician instructs the customer to run nslookup from the command prompt. What does the technician suspect is causing the customer's problem?
• improper IP address configuration on the host
• hardware failure of the ISR used to connect the customer to the ISP
• bad cables or connections at the customer site
• failure of DNS to resolve names to IP addresses
20. Which layers of the OSI model are commonly referred to as the upper layers?
• application, presentation, session
• application, session, network
• presentation, transport, network
• presentation, network, data link
• session, transport, network
Labels: CCNA Discovery 2
CCNA Discovery 2 Module 1 Exam Answers V4.0
0 comments Posted by GOSSIP - HOT 247 [d0t] Us at 12:58 PM
• the number of routers between the source and destination device
• the IP address of the router nearest the destination device
• the average time it takes a packet to reach the destination and for the response to return to the source
• whether or not the destination device is reachable through the network
• the average time it takes each router in the path between source and destination to respond
2. What are three main types of high-bandwidth connection options used by medium- to large-sized businesses? (Choose three.)
• DSL
• cable modem
• Ethernet
• metro Ethernet
• T1
• T3
3. What is the maximum T1 transmission speed?
• 56 kbps
• 128 kbps
• 1.544 Mbps
• 2.4 Mbps
4. Which of the following start the test of destination reachability?
• echo request issued by source
• echo reply issued by source
• echo request issued by destination
• echo reply issued by destination
5. Which statement describes a function of a Tier 1 ISP?
• peers with other similarly sized ISPs to form the global Internet backbone
• uses the services of Tier 3 ISPs to connect to the global Internet backbone
• pays Tier 2 ISPs for transit services to connect across continents
• limits the offered services to small geographic areas
6. At which point do individuals and small businesses connect directly to the ISP network to obtain Internet access?
• at a POP
• at an IXP
• at a Metro Ethernet link
• on the ISP extranet
7. What information is contained in the numbered RFCs maintained by the IETF?
• the rules for acceptable use of websites and e-mail
• the descriptions of various hardware components that connect to the Internet
• the specifications and rules for how devices communicate over an IP network
• the standards for cabling and wiring for local Ethernet networks
8. Which network support services team is responsible for testing a new customer connection and for monitoring the ongoing operation of the link?"
• customer service
• help desk
• network operations
• on-site installation
9. Which network support services team identifies whether the client site has existing network hardware and circuits installed?
• customer service
• help desk
• network operations
• planning and provisioning
10. Which ISP network support systems team will typically contact the customer once a new circuit is ready and guide the customer in setting up passwords and other account information?
• help desk
• customer service
• network operations center
• on-site installation team
• planning and provisioning
11. What feature allows network devices to be scalable?
• a fixed number of interfaces
• ease of repair
• modularity
• low maintenance requirements
• low cost
12. Which command generated this output?
• 1 12.0.0.2 4 msec 4 msec 4 msec
• 2 23.0.0.3 20 msec 16 msec 16 msec
• 3 34.0.0.4 16 msec 18 msec 16 msec
• Router# traceroute 34.0.0.4
• Router# nslookup 34.0.0.4
• Router# ping 34.0.0.4
• Router# telnet 34.0.0.4
13. Which network utility helps determine the location of network problems and identifies routers that packets travel across?
• ping
• ipconfig
• traceroute
• ixp
14. What interconnects the Internet backbone?
• gateway routers
• IXPs
• POPs
• satellite dishes
15. What units are used to measure Internet bandwidth?
• bits per second
• bytes per second
• hertz
• megabytes per second
• packets per second
16. The IT manager of a medium-sized business wishes to house the company-owned web servers in a facility that offers round-the-clock controlled access, redundant power, and high-bandwidth Internet access. Which ISP service will fulfill this need?
• web hosting
• planning and provisioning
• application hosting
• equipment colocation
• Tier 1 ISP services
17. What is the purpose of an RFC?
• to provide the connection point for multiple ISPs to the Internet
• to document the development and approval of an Internet standard
• to connect a business to an ISP
• to provide data communication services to ISP customers
• to monitor network performance and connection status of ISP clients
18. When did the Internet become available for use by businesses and consumers?
• 1979
• 1984
• 1991
• 1999
• 2000
19. What was the original purpose of the Internet?
• voice communication
• marketing
• research
• commerce
20. What three support service teams are commonly found within an ISP? (Choose three.)
• help desk
• computer support
• application readiness
• network operations center
• planning and provisioning
• implementation and documentation
Labels: CCNA Discovery 2
CCNA Discovery 1 Module 9 Exam Answers V4.0
0 comments Posted by GOSSIP - HOT 247 [d0t] Us at 12:56 PM
• Reboot the web server.
• Replace the NIC of the computer.
• Ask the user to log off and log on again.
• Ask the user what URL has been typed and what error message displays.
2. A customer called the cable company to report that the Internet connection is unstable. After trying several configuration changes, the technician decided to send the customer a new cable modem to try. What troubleshooting technique does this represent?
• top-down
• bottom-up
• substitution
• trial-and-error
• divide-and-conquer
3. Only one workstation on a particular network cannot reach the Internet. What is the first troubleshooting step if the divide-and-conquer method is being used?
• Check the NIC, and then check the cabling.
• Check the workstation TCP/IP configuration.
• Test all cables, and then test layer by layer up the OSI model.
• Attempt to Telnet, and then test layer by layer down the OSI model.
4. Which two troubleshooting techniques are suitable for both home networks and large corporate networks? (Choose two.)
• having a backup ISR
• running network monitoring applications
• documenting the troubleshooting process
• keeping a record of system upgrades and software versions
• keeping spare switches, routers, and other equipment available
5. Identify two physical-layer network problems. (Choose two.)
• hardware failure
• software configuration
• devices not able to ping
• loose cable connections
• device driver configuration
6. Which ipconfig command requests IP configuration from a DHCP server?
• ipconfig
• ipconfig /all
• ipconfig /renew
• ipconfig /release
7. What command is used to determine the location of delay for a packet traversing the Internet?
• ipconfig
• netstat
• nslookup
• ping
• tracert
8. What command is used to determine if a DNS server is providing name resolution?
• ipconfig
• netstat
• nslookup
• tracert
9. Which troubleshooting method begins by examining cable connections and wiring issues?
• top-down
• bottom-up
• substitution
• divide-and-conquer
10. A technician suspects that a Linksys integrated router is the source of a network problem. While troubleshooting, the technician notices a blinking green activity LED on some of the ports. What does this indicate?
• Self-diagnostics have not completed.
• The power supply is the source of the problem.
• The ports are operational and are receiving traffic.
• The ports are operational, but no traffic is flowing.
• There are no cables plugged into those ISR ports.
• The ports have cables plugged in, but they are not functional.
11. A PC is plugged into a switch and is unable to connect to the network. The UTP cable is suspected. What could be the problem?
• A straight-through cable is being used
• The connectors at both ends of the cable are RJ-45.
• The RJ-45 connectors are crimped onto the cable jacket.
• A crossover cable is being used.
12. Refer to the graphic. What configuration is incorrect in the network shown?
• The host IP address is incorrect.
• The host subnet mask is incorrect.
• The host default gateway is incorrect.
• The wired connection is the wrong type of cable.
• The Linksys integrated router does not support wireless.
13. Which three settings must match on the client and access point for a wireless connection to occur? (Choose three.)
• SSID
• authentication
• MD5 checksum
• antennae type
• encryption key
• MAC address filters
14. A technician is troubleshooting a security breach on a new wireless access point. Which three configuration settings make it easy for hackers to gain access? (Choose three.)
• configuring NAT
• broadcasting the SSID
• using open authentication
• enabling MAC address filters
• using the default internal IP address
• using DHCP to provide IP addresses
15. Refer to the graphic. The wireless host cannot access the Internet, but the wired host can. What is the problem?
• The host WEP key is incorrect.
• The host IP address is incorrect.
• The host subnet mask is incorrect.
• The host default gateway is incorrect.
• The integrated router internal IP address is incorrect.
• The integrated router Internet IP address is incorrect.
16. Refer to the graphic. What configuration is incorrect in the network shown?
• The host IP address is incorrect.
• The host subnet mask is incorrect.
• The host default gateway is incorrect.
• The wired connection is the wrong type of cable.
• The Linksys integrated router does not support wireless.
17. When acting as a DHCP server, what three types of information can an ISR provide to a client? (Choose three.)
• physical address
• MAC address
• default gateway
• static IP address
• dynamic IP address
• DNS server address
18. What two items could be checked to verify connectivity between the router and the ISP? (Choose two.)
• router status page
• wireless card settings
• router operating system version
• local host operating system version
• connectivity status as indicated by LEDs
19. A technician is unsuccessful in establishing a console session between a PC and a Linksys integrated router. Both devices have power, and a cable is connected between them. Which two troubleshooting steps could help to diagnose this problem? (Choose two.)
• Ensure the correct cable is used.
• Ensure the SSID is the same on both devices.
• Ensure both devices have the same IP address.
• Ensure both devices have different subnet masks.
• Ensure the encryption type on both devices match.
• Ensure the link status LED on the integrated router is lit.
20. Network baselines should be performed in which two situations? (Choose two.)
• after the network is installed and running optimally
• after a virus outbreak is discovered on the network
• after major changes are implemented on the network
• after several computers are added to the network
• at the end of the work week
21. Typically, help desk personnel assist end users in which two tasks? (Choose two.)
• identifying when the problem occurred
• determining if other users are currently logged into the computer
• updating network diagrams and documentation
• implementing the solution to the problem
• running a network baseline test
• determining the cost of fixing the problem
22. How does remote-access software help in the troubleshooting process?
• Remote access uses a live chat feature.
• Users have to be present so that they can view LEDs and change cables if necessary.
• Diagnostics can be run without a technician being present at the site.
• FAQs can be consulted more easily.
23. Which two items should be added to the documentation following a troubleshooting event? (Choose two.)
• final resolution
• repetitive measures
• number of people involved in the problem
• accurate current network infrastructure diagrams
• results of successful and unsuccessful troubleshooting steps
Labels: CCNA Discovery 1
CCNA Discovery 1 Module 8 Exam Answers V4.0
0 comments Posted by GOSSIP - HOT 247 [d0t] Us at 12:55 PM
• fishing
• vishing
• phishing
• spamming
• pretexting
• junk mailing
2. During a pretexting event, how is a target typically contacted?
• by e-mail
• by phone
• in person
• through another person
3. While surfing the Internet, a user notices a box claiming a prize has been won. The user opens the box unaware that a program is being installed. An intruder now accesses the computer and retrieves personal information. What type of attack occurred?
• worm
• virus
• Trojan horse
• denial of service
4. What is a major characteristic of a Worm?
• malicious software that copies itself into other executable programs
• tricks users into running the infected software
• a set of computer instructions that lies dormant until triggered by a specific event
• exploits vulnerabilities with the intent of propagating itself across a network
5. A flood of packets with invalid source-IP addresses requests a connection on the network. The server busily tries to respond, resulting in valid requests being ignored. What type of attack occurred?
• Trojan horse
• brute force
• ping of death
• SYN flooding
6. What type of advertising is typically annoying and associated with a specific website that is being visited?
• adware
• popups
• spyware
• tracking cookies
7. What is a widely distributed approach to marketing on the Internet that advertises to as many individual users as possible via IM or e-mail?
• brute force
• spam
• spyware
• tracking cookies
8. What part of the security policy states what applications and usages are permitted or denied?
• identification and authentication
• remote access
• acceptable use
• incident handling
9. Which statement is true regarding anti-virus software?
• Only e-mail programs need to be protected.
• Only hard drives can be protected.
• Only after a virus is known can an anti-virus update be created for it.
• Only computers with a direct Internet connection need it.
10. Which two statements are true concerning anti-spam software? (Choose two.)
• Anti-spam software can be loaded on either the end-user PC or the ISP server, but not both.
• When anti-spam software is loaded, legitimate e-mail may be classified as spam by mistake.
• Installing anti-spam software should be a low priority on the network.
• Even with anti-spam software installed, users should be careful when opening e-mail attachments.
• Virus warning e-mails that are not identified as spam via anti-spam software should be forwarded to other users immediately.
11. What term is used to describe a dedicated hardware device that provides firewall services?
• server-based
• integrated
• personal
• appliance-based
12. Which acronym refers to an area of the network that is accessible by both internal, or trusted, as well as external, or untrusted, host devices?
• SPI
• DMZ
• ISR
• ISP
13. Which statement is true about port forwarding within a Linksys integrated router?
• Only external traffic that is destined for specific internal ports is permitted. All other traffic is denied.
• Only external traffic that is destined for specific internal ports is denied. All other traffic is permitted.
• Only internal traffic that is destined for specific external ports is permitted. All other traffic is denied.
• Only internal traffic that is destined for specific external ports is denied. All other traffic is permitted.
14. To which part of the network does the wireless access point part of a Linksys integrated router connect?
• DMZ
• external
• internal
• a network other than the wired network
15. Refer to the graphic. What is the purpose of the Internet Filter option of Filter IDENT (Port 113. on the Linksys integrated router?
• to require a user ID and password to access the router
• to prevent outside intruders from attacking the router through the Internet
• to require a pre-programmed MAC address or IP address to access the router
• to disable tracking of internal IP addresses so they cannot be spoofed by outside devices
16. What statement is true about security configuration on a Linksys integrated router?
• A DMZ is not supported.
• The router is an example of a server-based firewall.
• The router is an example of an application-based firewall.
• Internet access can be denied for specific days and times.
17. What environment would be best suited for a two-firewall network design?
• a large corporate environment
• a home environment with 10 or fewer hosts
• a home environment that needs VPN access
• a smaller, less congested business environment
18. What is one function that is provided by a vulnerability analysis tool?
• It provides various views of possible attack paths.
• It identifies missing security updates on a computer.
• It identifies wireless weak points such as rogue access points.
• It identifies all network devices on the network that do not have a firewall installed.
• It identifies MAC and IP addresses that have not been authenticated on the network.
19. Many best practices exist for wired and wireless network security. The list below has one item that is not a best practice. Identify the recommendation that is not a best practice for wired and wireless security.
• Periodically update anti-virus software.
• Be aware of normal network traffic patterns.
• Periodically update the host operating system.
• Activate the firewall on a Linksys integrated router.
• Configure login permissions on the integrated router.
• Disable the wireless network when a vulnerability analysis is being performed.
20. What best practice relates to wireless access point security?
• activation of a popup stopper
• a change of the default IP address
• an update in the antivirus software definitions
• physically securing the cable between the access point and client
21. Refer to the graphic. In the Linksys Security menu, what does the SPI Firewall Protection option Enabled provide?
• It prevents packets based on the application that makes the request.
• It allows packets based on approved internal MAC or IP addresses.
• It requires that packets coming into the router be responses to internal host requests.
• It translates an internal address or group of addresses into an outside, public address.
Labels: CCNA Discovery 1
CCNA Discovery 1 Module 7 Exam Answers V4.0
0 comments Posted by GOSSIP - HOT 247 [d0t] Us at 12:55 PM
• transmits at much lower frequencies
• has higher power output
• transmits at much higher frequencies
• uses better encryption methods
2. What are three advantages of wireless over wired technology? (Choose three.)
• more secure
• longer range
• anytime, anywhere connectivity
• easy and inexpensive to install
• ease of using licensed air space
• ease of adding additional devices
3. What are two benefits of wireless networking over wired networking? (Choose two.)
• speed
• security
• mobility
• reduced installation time
• allows users to share more resources
• not susceptible to interference from other devices
4. A technician has been asked to provide wireless connectivity to the wired Ethernet network of a building. Which three factors affect the number of access points needed? (Choose three.)
• the size of the building
• the number of solid interior walls in the building
• the presence of microwave ovens in several offices
• the encryption method used on the wireless network
• the use of both Windows and Appletalk operating systems
• the use of shortwave or infrared on the AP
5. Why is security so important in wireless networks?
• Wireless networks are typically slower than wired networks.
• Televisions and other devices can interfere with wireless signals.
• Wireless networks broadcast data over a medium that allows easy access.
• Environmental factors such as thunderstorms can affect wireless networks.
6. What does the Wi-Fi logo indicate about a wireless device?
• IEEE has approved the device.
• The device is interoperable with all other wireless standards.
• The device is interoperable with other devices of the same standard that also display the Wi-Fi logo.
• The device is backwards compatible with all previous wireless standards.
7. Which statement is true concerning wireless bridges?
• connects two networks with a wireless link
• stationary device that connects to a wireless LAN
• allows wireless clients to connect to a wired network
• increases the strength of a wireless signal
8. Which WLAN component is commonly referred to as an STA?
• cell
• antenna
• access point
• wireless bridge
• wireless client
9. Which statement is true concerning an ad-hoc wireless network?
• created by connecting wireless clients in a peer-to-peer network
• created by connecting wireless clients to a single, centralized AP
• created by connecting multiple wireless basic service sets through a distribution system
• created by connecting wireless clients to a wired network using an ISR
10. Refer to the graphic. In the Wireless menu option of a Linksys integrated router, what does the Network Mode option Mixed mean?
• The router supports encryption and authentication.
• The router supports both wired and wireless connections.
• The router supports 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n devices.
• The router supports connectivity through infrared and radio frequencies.
11. Refer to the graphic. In the Wireless menu of a Linksys integrated router, what configuration option allows the presence of the access point to be known to nearby clients?
• Network Mode
• Network Name (SSID)
• Radio Band
• Wide Channel
• Standard Channel
• SSID Broadcast
12. Which two statements about a service set identifier (SSID) are true? (Choose two.)
• tells a wireless device to which WLAN it belongs
• consists of a 32-character string and is not case sensitive
• responsible for determining the signal strength
• all wireless devices on the same WLAN must have the same SSID
• used to encrypt data sent across the wireless network
13. Which two statements characterize wireless network security? (Choose two.)
• Wireless networks offer the same security features as wired networks.
• Wardriving enhances security of wireless networks.
• With SSID broadcast disabled, an attacker must know the SSID to connect.
• Using the default IP address on an access point makes hacking easier.
• An attacker needs physical access to at least one network device to launch an attack.
14. What type of authentication does an access point use by default?
• Open
• PSK
• WEP
• EAP
15. Which statement is true about open authentication when it is enabled on an access point?
• requires no authentication
• uses a 64-bit encryption algorithm
• requires the use of an authentication server
• requires a mutually agreed upon password
16. What are two authentication methods that an access point could use? (Choose two.)
• WEP
• WPA
• EAP
• ASCII
• pre-shared keys
17. What is the difference between using open authentication and pre-shared keys?
• Open authentication requires a password. Pre-shared keys do not require a password.
• Open authentication is used with wireless networks. Pre-shared keys are used with wired networks.
• Pre-shared keys require an encrypted secret word. Open authentication does not require a secret word.
• Pre-shared keys require a MAC address programmed into the access point. Open authentication does not require this programming.
18. What term describes the encoding of wireless data to prevent intercepted data from being read by a hacker?
• address filtering
• authentication
• broadcasting
• encryption
• passphrase encoding
19. What access-point feature allows a network administrator to define what type of data can enter the wireless network?
• encryption
• hacking block
• traffic filtering
• MAC address filtering
• authentication
20. What are the two WEP key lengths? (Choose two.)
• 8 bit
• 16 bit
• 32 bit
• 64 bit
• 128 bit
21. Complete the following sentence: WEP is used to ______ , and EAP is used to _____ wireless networks.
• encrypt; authenticate users on
• filter traffic; select the operating frequency for
• identify the wireless network; compress data on
• create the smallest wireless network; limit the number of users on
Labels: CCNA Discovery 1
CCNA Discovery 1 Module 6 Exam Answers V4.0
0 comments Posted by GOSSIP - HOT 247 [d0t] Us at 12:54 PM
• the IP address of a web server
• a physical network address
• the closest router interface to the source
• the source IP address in the data transmission
2. What type of server would use IMAP?
• DNS
• DHCP
• FTP
• Telnet
• web
3. Which type of server would most likely be used first by a network client in a corporate environment?
• DNS
• DHCP
• FTP
• Telnet
• web
4. Which protocol is used by FTP to transfer files over the Internet?
• TCP
• SMTP
• UDP
• SNMP
5. Which protocols are TCP/IP application layer protocols? (Choose two.)
• UDP
• FTP
• IP
• SMTP
• TCP
6. Which of the following are layers of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
• Application
• Physical
• Internet
• Network Access
• Presentation
7. You are creating a network-based video game. What influences your decision about which transport protocol to use for the application?
• UDP will not disrupt the game to retransmit dropped packets.
• TCP provides extra acknowledgements that will ensure smooth video delivery.
• Both TCP and UDP can be used simultaneously to ensure speed and guaranteed delivery.
• Both TCP and UDP may slow transmission and disrupt game operation, so no transport protocol should be used.
8. Whenever e-mail clients send letters, what device is used to translate the domain names into their associated IP addresses?
• Uniform Resource Locator
• Network redirector server
• SNMP server
• DNS server
9. Which application is most likely used to translate www.cisco.com to 198.133.219.25?
• DHCP
• DNS
• FTP
• HTTP
• POP
• SMTP
10. Refer to the graphic. Which protocol is used to access this website?
• IM
• FTP
• HTTP
• SNMP
• VoIP
11. Which port number is used by SMTP?
• 20
• 21
• 25
• 26
• 110
12. Which protocol is used by e-mail servers to communicate with each other?
• FTP
• HTTP
• TFTP
• SMTP
• POP
• SNMP
13. What client software enables logged in users to communicate with other logged in users in real time?
• blog
• web mail
• instant messaging
14. An Internet server is running both FTP and HTTP services. How does the server know which of these applications should handle an incoming segment?
• The packet header identifies it as an HTTP or FTP packet.
• The data in the segment is specially formatted for either HTTP or FTP.
• The segment destination port number identifies the application that should handle it.
• The source port number is associated with one of these well known server applications.
15. What term is used to describe how TCP/IP protocols are layered and interact to format, address, and transmit information across a network?
• protocol hierarchy
• protocol modeling
• protocol stack
• protocol layering
16. What three items are contained in an Ethernet frame? (Choose three.)
• source IP address
• source MAC address
• destination IP address
• destination MAC address
• error-checking information
17. What information is contained in an IP header?
• source and destination IP addresses
• source and destination MAC addresses
• only destination IP and MAC addresses
• both source and destination IP and MAC addresses
18. Cabling issues are associated with which OSI layer?
• 4
• 2
• 1
• 3
19. A device receives an Ethernet frame and recognizes the MAC address as its own. What does the device do to the message to get to the encapsulated data?
• removes the IP header
• removes the TCP header
• passes data to the application layer
• removes the Ethernet header and trailer
20. A client has decoded a frame and started the de-encapsulation process. In which order does the de-encapsulation process occur?
• 1) remove IP header
2) remove Ethernet header and trailer
3) remove TCP header
4) pass data to the application
• 1) add TCP header to data
2) add an IP header
3) add frame header and trailer
4) encode the frame into bits
• 1) remove Ethernet header and trailer
2) remove IP header
3) remove TCP header
4) pass data to the application
• 1) add TCP header to data
2) add Ethernet header and trailer
3) add an IP header
4) encode the frame into bits
21. What is an advantage of the use of layers in the OSI reference model?
• It breaks network communications into larger parts.
• It increases complexity.
• It prevents changes in one layer from affecting other layers.
• It requires the use of single-vendor equipment for hardware and software communications.
22. What is the correct order of the layers of the OSI reference model, starting at the lowest layer and working up the model?
• data link, physical, transport, network, presentation, session, application
• physical, data link, network, session, transport, presentation, application
• physical, data link, network, transport, presentation, session, application
• physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, application
• application, session, presentation, transport, data link, network, physical
Labels: CCNA Discovery 1
CCNA Discovery 1 Module 5 Exam Answers V4.0
0 comments Posted by GOSSIP - HOT 247 [d0t] Us at 12:54 PM
• 8 bits
• 16 bits
• 32 bits
• 64 bits
• 128 bits
2. Refer to the graphic. A user at the workstation cannot connect to the server. All cables have been tested and are working and all devices have IP addressing. However, the user cannot ping the server. What is causing the problem?
• The router interface does not have a default gateway.
• The switch does not have an IP address and default gateway.
• The workstation and server are on different logical networks.
• The workstation does not know the MAC address of the switch.
3. Which part of an IP address identifies a specific device on a network?
• first two octets
• third and fourth octets
• network portion
• host portion
• only the fourth octet
4. Given a host with the IP address 172.32.65.13 and a default subnet mask, to which network does the host belong?
• 172.32.65.0
• 172.32.65.32
• 172.32.0.0
• 172.32.32.0
5. Which default subnet mask provides the most host bits?
• 255.0.0.0
• 255.255.0.0
• 255.255.255.0
• 255.255.255.252
6. How many bits are available for Class B host IP addresses using a default subnet mask?
• 4
• 8
• 16
• 24
7. How many usable hosts are available given a Class C IP address with the default subnet mask?
• 254
• 255
• 256
• 510
• 511
• 512
8. Assuming a default mask, which portion of the IP address 175.124.35.4 represents the host?
• 175.124
• 35.4
• .4
• 124.35.4
• 175.124.35
9. Which of the following are private IP addresses? (Choose three.)
• 10.1.1.1
• 172.32.5.2
• 192.167.10.10
• 172.16.4.4
• 192.168.5.5
• 224.6.6.6
10. What destination IP address is used in a unicast packet?
• a specific host
• a group of hosts
• the default gateway
• the network broadcast address
11. What is the destination MAC address in a multicast Ethernet frame?
• the MAC address of the sending host
• the MAC address of the destination host
• an address that begins with 01-00-5E in hexadecimal
• a 48-bit hexadecimal address expressed as FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
12. Yvonne is talking to her friend on the phone. What type of message is this?
• broadcast
• simulcast
• multicast
• unicast
13. What information must be included within a unicast message for it to be delivered on an Ethernet network?
• MAC and IP addresses for the default router
• IP address and subnet mask of the default gateway
• MAC and IP addresses that correspond to a destination group
MAC and IP addresses that correspond to a specific destination host
14. A PC obtains its IP address from a DHCP server. If the PC is taken off the network for repair, what happens to the IP address configuration?
• The configuration is permanent and nothing changes.
• The address lease is automatically renewed until the PC is returned.
• The address is returned to the pool for reuse when the lease expires.
• The configuration is held by the server to be reissued when the PC is returned.
15. Which type of server dynamically assigns an IP address to a host?
• ARP
• DHCP
• DNS
• RARP
16. Which three statements describe a DHCP Discover message? (Choose three.)
• The source MAC address is 48 ones (FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF).
• The destination IP address is 255.255.255.255.
• The message comes from a server offering an IP address.
• The message comes from a client seeking an IP address.
• All hosts receive the message, but only a DHCP server replies.
• Only the DHCP server receives the message.
17. Refer to the graphic. A host connects to a Linksys integrated router that is also a DHCP server and receives an IP address from it. Which address does the host need to access the ISP and the Internet?
• IP address of the destination host
• public gateway IP address of the ISP
• external IP address of the integrated router that connects to the ISP
• internal IP address of the integrated router that connects to the local network
18. Which statement is true concerning private IP addresses?
• ensures that two networks separated by the Internet use unique IP network numbers
• allows internal hosts to communicate with servers across the Internet
• solves the issue of a finite number of available public IP addresses
• allows for ISPs to be able to quickly determine network location
19. What is one of the purposes of NAT?
• filters network traffic based on IP address ranges
• prevents external users from detecting the IP addresses used on a network
• inspects traffic that might be harmful or used in an attack against the network
• translates IP addresses into easy-to-remember domain names
20. Which two statements describe packets that are sent through a Linksys integrated router using NAT? (Choose two.)
• Packets that are sent to any destination need to be translated.
• Packets that are sent to hosts on the same network need to be translated.
• Packets that are sent to a destination outside the local network need to be translated.
• Packets that are sent to a destination outside a local network do not need to be translated.
• Packets that are sent between hosts on the same local network do not need to be translated.
21. Refer to the graphic. NAT and DHCP are installed on the Linksys integrated router. Which IP address is most likely to be assigned to the local computer, Host1?
• 10.0.0.17
• 128.107.1.2
• 192.135.250.0
• 209.165.201.1
Labels: CCNA Discovery 1
CCNA Discovery 1 Module 4 Exam Answers V4.0
0 comments Posted by GOSSIP - HOT 247 [d0t] Us at 12:53 PM
• a group of PCs connected together on a LAN
• a group of PCs connected together by an ISP
• a network of networks that connects countries around the world
• a worldwide collection of networks controlled by a single organization
2. What type of connection point is a point of presence (POP)?
• between a client and a host
• between two local networks
• between a computer and a switch
• between an ISP and a home-based LAN
3. What is the term for the group of high-speed data links that interconnect ISPs?
• Internet LAN
• ISP backbone
• Internet gateways
• Internet providers
• Internet backbone
4. Which device can act as a router, switch, and wireless access point in one package?
• hub
• bridge
• modem
• repeater
• ISR
5. What are three characteristics of business class ISP service? (Choose three.)
• fast connections
• extra web space
• free Windows upgrade
• cheapest cost available to all users
• additional e-mail accounts
• replacement hardware at no cost
6. What is a major characteristic of asymmetric Internet service?
• Download speeds and upload speeds are equal.
• Download speeds are slower than upload speeds.
• Upload speeds and download speeds are different.
• Upload speeds and download speeds are irrelevant.
7. Which three elements are required to successfully connect to the Internet? (Choose three.)
• an IP address
• file sharing enabled
• a network connection
• server services enabled
• access to an Internet service provider
• an address obtained directly from the RIR
8. What term describes each router through which a packet travels when moving between source and destination networks?
• NOC
• ISP
• hop
• segment
9. What does the tracert command test?
• NIC functionality
• the ISP bandwidth
• the network path to a destination
• the destination application functionality
10. What type of end-user connectivity requires that an ISP have a DSLAM device in their network?
• analog technology
• cable modem technology
• digital subscriber line technology
• wireless technology
11. Why would an ISP require a CMTS device on their network?
• to connect end users using cable technology
• to connect end users using analog technology
• to connect end users using wireless technology
• to connect end users using digital subscriber line technology
12. Refer to the graphic. What type of cabling is shown?
• STP
• UTP
• coax
• fiber
13. Refer to the graphic. What type of cabling is shown?
• STP
• UTP
• coax
• fiber
14. Which two places are most appropriate to use UTP cabling? (Choose two.)
• between buildings
• in a home office network
• where EMI is an issue
• in a cable TV network
• inside a school building
• in a manufacturing environment with hundreds of electrical devices
15. What does adherence to cabling standards ensure?
• data security
• no loss of signal
• no electromagnetic interference
• reliable data communications
16. Refer to the graphic. What type of cable is shown?
• crossover
• eight coax channels
• multimode fiber
• single-mode fiber
• straight-through
17. What connector is used to terminate Ethernet unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cabling?
• ST
• BNC
• RJ-11
• RJ-45
18. Which two characteristics describe copper patch panels? (Choose two.)
• uses RJ-11 jacks
• uses RJ-45 jacks
• supports only data transmissions
• allows quick rearrangements of network connections
• forwards transmissions based on MAC addresses
19. What are two advantages of cable management? (Choose two.)
• requires no preplanning
• aids in isolation of cabling problems
• protects cables from physical damage
• provides compliance with future standards
• provides a short-term solution for cable installation
20. What are two common causes of signal degradation when using UTP cabling? (Choose two.)
• installing cables in conduit
• having improper termination
• losing light over long distances
• installing low quality cable shielding
• using low quality cables or connectors
21. What are three commonly followed standards for constructing and installing cabling? (Choose three.)
• pinouts
• cable lengths
• connector color
• connector types
• cost per meter (foot)
• tensile strength of plastic insulator
Labels: CCNA Discovery 1
CCNA Discovery 1 Module 3 Exam Answers V4.0
0 comments Posted by GOSSIP - HOT 247 [d0t] Us at 12:53 PM
• flow control
• encapsulation
• encoding
• multicasting
• access method
2. Refer to the graphic. Five PCs are connected through a hub. If host H1 wants to reply to a message from host H2, which statement is true?
• H1 sends a unicast message to H2, but the hub forwards it to all devices.
• H1 sends a unicast message to H2, and the hub forwards it directly to H2.
• H1 sends a broadcast message to H2, and the hub forwards it to all devices.
• H1 sends a multicast message to H2, and the hub forwards it directly to H2.
3. Which two statements concerning networking standards are true? (Choose two.)
• adds complexity to networks
• encourages vendors to create proprietary protocols
• provides consistent interconnections across networks
• ensures that communications work best in a single-vendor environment
• simplifies new product development
4. What does the 100 mean when referencing the 100BASE-T Ethernet standard?
• type of cable used
• type of data transmission
• speed of transmission
• type of connector required
• maximum length of cable allowed
5. Which address does an NIC use when deciding whether to accept a frame?
• source IP address
• source MAC address
• destination IP address
• destination MAC address
• source Ethernet address
6. Which type of address is used in an Ethernet frame header?
• logical addresses only
• IP addresses only
• MAC addresses only
• broadcast addresses only
7. What is the function of the FCS field in an Ethernet frame?
• detects transmission errors
• provides timing for transmission
• contains the start of frame delimiter
• indicates which protocol will receive the frame
8. What is the purpose of logical addresses in an IP network?
• They identify a specific NIC on a host device.
• They are used to determine which host device accepts the frame.
• They provide vendor-specific information about the host.
• They are used to determine the network that the host is located on.
• They are used by switches to make forwarding decisions.
9. Which device accepts a message on one port and always forwards the message to all other ports?
• modem
• switch
• router
• hub
10. Which two networking devices are used to connect hosts to the access layer? (Choose two.)
• router
• hub
• switch
• server
• computer
11. Host A needs to learn the MAC address of Host B, which is on the same LAN segment. A message has been sent to all the hosts on the segment asking for the MAC address of Host B. Host B responds with its MAC address and all other hosts disregard the request. What protocol was used in this scenario?
• ARP
• DHCP
• DNS
• WINS
12. A switch receives a frame with a destination MAC address that is currently not in the MAC table. What action does the switch perform?
• It drops the frame.
• It sends out an ARP request looking for the MAC address.
• It floods the frame out of all active ports, except the origination port.
• It returns the frame to the sender.
13. What is a benefit of having a router within the distribution layer?
• prevents collisions on a local network
• keeps broadcasts contained within a local network
• controls which hosts have access to the network
• controls host-to-host traffic within a single local network
14. Refer to the graphic. What does the router do after it determines that a data packet from Network 1 should be forwarded to Network 2?
• It sends the data packet as it was received.
• It reassembles the frame with different MAC addresses than the original frame.
• It reassembles the data packet with different IP addresses than the original data packet.
• It reassembles both the packet and the frame with different destination IP and MAC addresses.
15. Which table does a router use to make decisions on where a data packet is to be sent?
• ARP table
• routing table
• network table
• forwarding table
16. If the default gateway is configured incorrectly on the host, what is the impact on communications?
• The host is unable to communicate on the local network.
• The host can communicate with other hosts on the local network, but is unable to communicate with hosts on remote networks.
• The host can communicate with other hosts on remote networks, but is unable to communicate with hosts on the local network.
• There is no impact on communications.
17. What device is typically used as the default gateway for a computer?
• a server hosted by the ISP
• the router interface closest to the computer
• a server managed by a central IT department
• the switch interface that connects to the computer
18. If a router receives a packet that it does not know how to forward, what type of route must be configured on the router to prevent the router from dropping it?
• dynamic route
• default route
• destination route
• default destination
19. Which two items are included in a network logical map? (Choose two.)
• naming scheme
• IP addressing scheme
• length of cable runs
• physical location of networking devices
• specific layout of interconnections between networking devices and hosts
20. An integrated router can normally perform the functions of which two other network devices? (Choose two.)
• NIC
• switch
• e-mail server
• application server
• wireless access point
21. What is a reason for disabling simple file sharing?
• It enables the user to map a remote resource with a local drive.
• It enables the user to share all files with all users and groups.
• It enables the user to share printers.
• It enables the user to set more specific security access levels.
Labels: CCNA Discovery 1
CCNA Discovery 1 Module 2 Exam Answers V4.0
0 comments Posted by GOSSIP - HOT 247 [d0t] Us at 12:52 PM
• clean install
• upgrade
• multi-boot
• virtualization
2. Which two statements should be included in a pre-installation checklist when upgrading an operating system? (Choose two.)
• Verify that the hardware resources have multiple partitions.
• Verify that the hardware resources meet or exceed the published minimum requirements.
• Complete a full backup of all important files and data.
• Overwrite any data currently contained on the drive to remove all contents.
• Verify that the hardware resources are certified to work with the existing operating system prior to upgrading.
3. Which three pieces of information must be specified on a computer to allow that computer to send and receive information across networks? (Choose three.)
• closest server
• operating system
• IP address
• subnet mask
• default gateway
• network card driver
4. Which two items must be unique to each computer and cannot be duplicated on a network? (Choose two.)
• partition
• file system
• computer name
• IP address
• operating system
5. Which method of interacting with an operating system involves typing commands at a command prompt?
• CLI
• GUI
• redirector
• kernel translator
6. What are three characteristics of an operating system that is released under the GPL (GNU Public License)? (Choose three.)
• full access to source code
• software often available free
• structured development cycle
• can be expensive to purchase
• limits what end-user can do with code
• support normally user-based and often free
7. What is the purpose of a default gateway?
• physically connects a computer to a network
• provides a permanent address to a computer
• identifies the network to which a computer is connected
• identifies the logical address of a networked computer and uniquely identifies it to the rest of the network
• identifies the device that allows local network computers to communicate with devices on other networks
8. Which two statements are true about drive partitions? (Choose two.)
• Partitions are necessary in multi-boot installations.
• A hard drive can be divided into an operating system partition and a data partition.
• User data is never overwritten when a drive is partitioned.
• A disk partition is a defined section of an operating system.
• Each partition requires a different file system type.
9. What occurs when computers are configured to receive their network configurations dynamically?
• Each computer receives a permanent IP address.
• A network administrator enters information on each computer.
• Each computer requests configuration information from a server.
• An NIC automatically provides configuration information to the computer and stores that configuration information.
10. What are two ways that a user can interact with an operating system shell? (Choose two.)
• CLI
• OS
• GUI
• NIC
• kernel
11. Which three resource specifications are given by the manufacturer to ensure that an operating system performs as designed? (Choose three.)
• required hard disk space
• type of accelerated graphics card
• recommended amount of RAM
• printer requirements
• processor type and speed
• type of keyboard
Labels: CCNA Discovery 1
CCNA Discovery 1 Module 1 Exam Answers V4.0
0 comments Posted by GOSSIP - HOT 247 [d0t] Us at 12:49 PM
• RAM
• CPU
• video card
• sound card
• operating system
2. What are two advantages of purchasing a preassembled computer? (Choose two.)
• usually a lower cost
• exact components may be specified
• extended waiting period for assembly
• adequate for performing most general applications
• suited for customers with special needs
3. A user plans to run multiple applications simultaneously on a computer. Which computer component is essential to accomplish this?
• RAM
• NIC
• video card
• sound card
• storage device
4. Which adapter card enables a computer system to exchange information with other systems on a local network?
• modem card
• controller card
• video card
• sound card
• network interface card
5. What is the main storage drive used by servers, desktops, and laptops?
• tape drive
• hard drive
• optical drive (DVD)
• floppy disk drive
6. Which component is designed to remove high-voltage spikes and surges from a power line so that they do not damage a computer system?
• CPU
• surge suppressor
• motherboard
• hard drive
7. What are two examples of output peripheral devices? (Choose two.)
• printer
• speakers
• flash drive
• external DVD
• external modem
8. What two functions does a UPS provide that a surge protector does not ? (Choose two.)
• protects the computer from voltage surges
• provides backup power from an internal battery
• protects the computer from sudden voltage spikes
• gives the user time to phone the electrical company
• gives the user time to safely shut down the computer if the power fails
• provides backup power through a generator provided by the wall outlet
9. What is a word processor?
• It is a physical computer component.
• It is a program designed to perform a specific function.
• It is a program that controls the computer resources.
• It is a functional part of an operating system.
10. What is the purpose of the ASCII code?
• translates bits into bytes
• interprets graphics digitally
• translates digital computer language into binary language
• represents letters, characters, and numbers with bits
11. Why do servers often contain duplicate or redundant parts?
• Servers require more power and thus require more components.
• Servers should be accessible at all times.
• Servers can be designed as standalone towers or rack mounted.
• Servers are required by networking standards to have duplicate parts.
12. What are two benefits of hooking up a laptop to a docking station? (Choose two.)
• Mobility is increased.
• An external monitor can be used.
• Alternate connectivity options may be available.
• The keyboard can be changed to a QWERTY-style keyboard.
• More wireless security options are available.
13. Applications can be grouped into general use software or industry specific software. What are two examples of industry specific software? (Choose two.)
• CAD
• presentation
• spreadsheet
• word processing
• medical practice management
• contacts/scheduling management
14. Which three terms describe different types of computers? (Choose three.)
• operating system
• network
• laptop
• desktop
• Windows
• mainframe
15. How is a server different from a workstation computer?
• The server works as a standalone computer.
• The server provides services to clients.
• The workstation has fewer applications installed.
• The workstation has more users who attach to it.
16. How many values are possible using a single binary digit?
• 1
• 2
• 4
• 8
• 9
• 16
17. What measurement is commonly associated with computer processing speed?
• bits
• pixels
• hertz
• bytes
18. What can be used to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD)?
• dry and non humid conditions
• carpeted floor
• grounding strap
• uncluttered work space
19. If a peripheral device is not functioning, what are three things you should do to solve the problem? (Choose three.)
• Use the testing functionality on the peripheral itself, if available.
• Verify that all cables are connected properly.
• Disconnect all cables connected to the computer except those connected to the peripheral.
• Ensure that the peripheral is powered on.
• Disconnect the peripheral and verify that the computer is operating normally.
• Reload the computer operating system.
20. Which two steps should be performed when installing a peripheral device? (Choose two.)
• Download and install the most current driver.
• Connect the peripheral using any cable and any available port on the computer.
• Connect the peripheral using an appropriate cable or wireless connection.
• Test the peripheral on another machine before installing it on the one where it will be used.
• Check the computer documentation to see if the peripheral vendor is compatible with the PC vendor.
21. In newer operating systems, how are system resources assigned by default when components are installed?
• manually assigned by the operating system
• manually assigned by the administrator
• statically assigned by the component to a preset resource
• dynamically assigned between the component and the operating system
Labels: CCNA Discovery 1